Constrained smoother
Source code on Github.
A smoother plugin for nav2_smoother based on the original deprecated smoother in nav2_smac_planner and put into operational state by RoboTech Vision. Suitable for applications which need planned global path to be pushed away from obstacles and/or for Reeds-Shepp motion models. It optimizes for path length, smoothness, distance from obstacles, and curvature in a large Ceres-based optimization program.
Important note: Constrained smoother uses a rather heavy optimization algorithm and thus is suggested to be used on a periodically truncated path. TruncatePathLocal BT Node can be used for achieving a proper path length and DistanceController BT Node can be used for achieving periodicity.
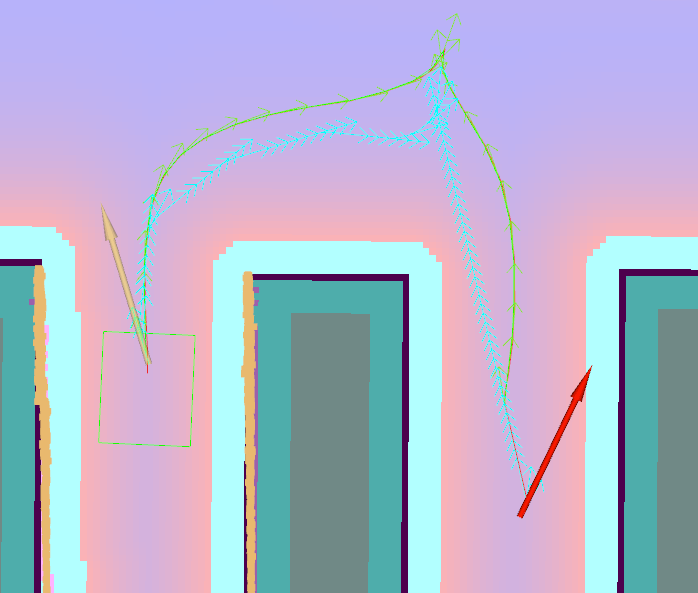
Following image depicts how Constrained Smoother can improve quality of an input path (cyan, generated by an outdated version of Smac Planner, intentionally not configured optimally to highlight the power of the smoother), increasing its smoothness and distance from obstacles. Resulting path is marked by green color. Note: last few path poses are not smoothed since TruncatePathLocal is used on this path.

Smoother Server Parameters
- reversing_enabled
Type
Default
bool
true
- Description
Whether to detect forward/reverse direction and cusps. Should be set to false for paths without orientations assigned
- path_downsampling_factor
Type
Default
int
1
- Description
Every n-th node of the path is taken for optimization. Useful for speed-up
- path_upsampling_factor
Type
Default
int
1
- Description
Upsampling factor for refining. 0 - path remains downsampled (see
path_downsampling_factor), 1 - path is upsampled back to original granularity using cubic bezier, 2… - more upsampling
- keep_start_orientation
Type
Default
bool
true
- Description
Whether to prevent the start orientation from being smoothed
- keep_goal_orientation
Type
Default
bool
true
- Description
Whether to prevent the goal orientation from being smoothed
- minimum_turning_radius
Type
Default
double
0.4
- Description
Minimum turning radius the robot can perform. Can be set to 0.0 (or w_curve can be set to 0.0 with the same effect) for diff-drive/holonomic robots
- w_curve
Type
Default
double
30.0
- Description
Weight to enforce minimum_turning_radius
- w_dist
Type
Default
double
0.0
- Description
Weight to bind path to original as optional replacement for cost weight
- w_smooth
Type
Default
double
2000000.0
- Description
Weight to maximize smoothness of path
- w_cost
Type
Default
double
0.015
- Description
Weight to steer robot away from collision and cost
- w_cost_cusp_multiplier
Type
Default
double
3.0
- Description
Option to use higher weight during forward/reverse direction change, helping optimizer to converge or add an extra obstacle avoidance at these problematic segments. Following image depicts improvement of the path with
w_cost_cusp_multiplier(green) compared to one without it (purple). Original path has cyan color.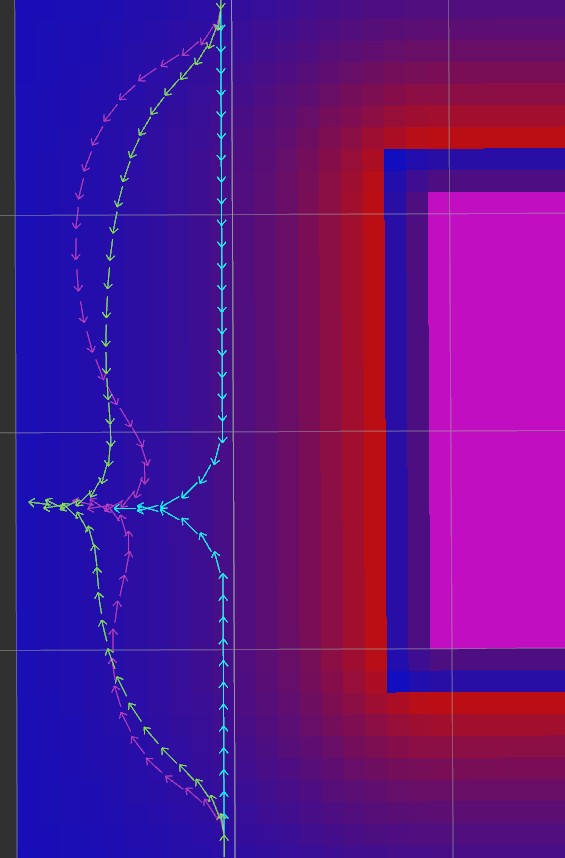
- cusp_zone_length
Type
Default
double
2.5
- Description
Length of the section around cusp in which nodes use
w_cost_cusp_multiplier(w_cost rises gradually inside the zone towards the cusp point, whose costmap weight eqals w_cost*w_cost_cusp_multiplier)
- cost_check_points
Type
Default
array of double
[]
- Description
Points in robot frame to grab costmap values from. Format: [x1, y1, weight1, x2, y2, weight2, …].
IMPORTANT: Requires much higher number of optimizer iterations to actually improve the path. Use only if you really need it (highly elongated/asymmetric robots)
Following image depicts how two cost check points can be used to improve cost awareness of a rectangular robot.
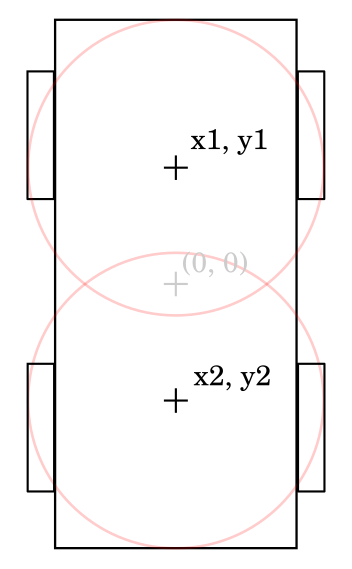
- optimizer.max_iterations
Type
Default
int
100
- Description
Maximum number of optimizer iterations
- optimizer.debug_optimizer
Type
Default
bool
false
- Description
Whether to print optimizer debug info
- optimizer.linear_solver_type
Type
Default
string
“SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY”
- Description
Linear solver type to be used by optimizer. Valid values are
SPARSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKYandDENSE_QR
- optimizer.gradient_tol
Type
Default
bool
1e-10
- Description
Gradient tolerance optimization termination criterion
- optimizer.fn_tol
Type
Default
bool
1e-7
- Description
Function tolerance optimization termination criterion
- optimizer.param_tol
Type
Default
bool
1e-15
- Description
Parameter tolerance optimization termination criterion
Example
smoother_server:
ros__parameters:
smoother_plugins: ["SmoothPath"]
SmoothPath:
plugin: "nav2_constrained_smoother/ConstrainedSmoother"
reversing_enabled: true # whether to detect forward/reverse direction and cusps. Should be set to false for paths without orientations assigned
path_downsampling_factor: 3 # every n-th node of the path is taken. Useful for speed-up
path_upsampling_factor: 1 # 0 - path remains downsampled, 1 - path is upsampled back to original granularity using cubic bezier, 2... - more upsampling
keep_start_orientation: true # whether to prevent the start orientation from being smoothed
keep_goal_orientation: true # whether to prevent the gpal orientation from being smoothed
minimum_turning_radius: 0.40 # minimum turning radius the robot can perform. Can be set to 0.0 (or w_curve can be set to 0.0 with the same effect) for diff-drive/holonomic robots
w_curve: 30.0 # weight to enforce minimum_turning_radius
w_dist: 0.0 # weight to bind path to original as optional replacement for cost weight
w_smooth: 2000000.0 # weight to maximize smoothness of path
w_cost: 0.015 # weight to steer robot away from collision and cost
# Parameters used to improve obstacle avoidance near cusps (forward/reverse movement changes)
w_cost_cusp_multiplier: 3.0 # option to use higher weight during forward/reverse direction change which is often accompanied with dangerous rotations
cusp_zone_length: 2.5 # length of the section around cusp in which nodes use w_cost_cusp_multiplier (w_cost rises gradually inside the zone towards the cusp point, whose costmap weight eqals w_cost*w_cost_cusp_multiplier)
# Points in robot frame to grab costmap values from. Format: [x1, y1, weight1, x2, y2, weight2, ...]
# IMPORTANT: Requires much higher number of iterations to actually improve the path. Uncomment only if you really need it (highly elongated/asymmetric robots)
# cost_check_points: [-0.185, 0.0, 1.0]
optimizer:
max_iterations: 70 # max iterations of smoother
debug_optimizer: false # print debug info
gradient_tol: 5e3
fn_tol: 1.0e-15
param_tol: 1.0e-20