Navigating with Speed Limits
Overview
This tutorial shows how to simply utilize Speed Filter which is designed to limit the maximum speed of robots in speed restriction areas marked on a map. This functionality is being covered by SpeedFilter costmap filter plugin which will be enabled and used in this document.
Requirements
It is assumed that ROS 2, Gazebo and TurtleBot4 packages are installed or built locally. Please make sure that the Nav2 project is also built locally as it was made in Build and Install.
Tutorial Steps
1. Prepare filter mask
As was written in Navigation Concepts, any Costmap Filter (including Speed Filter) is reading the data marked in a filter mask file. All information about filter masks, their types, detailed structure and how to make a new one is written in a Navigating with Keepout Zones tutorial at 1. Prepare filter masks chapter. The principal of drawing the filter mask for Speed Filter is the same as for Keepout Filter (to annotate a map with the requested zones), except that OccupancyGrid mask values have another meaning: these values are encoded speed limits for the areas corresponding to the cell on map.
Let’s look, how it is being decoded. As we know, OccupancyGrid values are belonging to the [0..100] range. For Speed Filter 0 value means no speed limit in the area corresponding zero-cell on mask. Values from [1..100] range are being linearly converted into a speed limit value by the following formula:
speed_limit = filter_mask_data * multiplier + base;
where:
filter_mask_data- is anOccupancyGridvalue of the corresponding cell on mask where maximum speed should be restricted.
baseandmultiplierare coefficients taken fromnav2_msgs/CostmapFilterInfomessages published by Costmap Filter Info Server (see in next chapter below).
The decoded speed_limit value may have one of two meanings:
Speed limit expressed in a percent from maximum robot speed.
Speed limit expressed in absolute values (e.g. in
m/s).
The meaning used by Speed Filter is being read from nav2_msgs/CostmapFilterInfo messages.
In this tutorial we will use the first type of speed restriction expressed in a percent from maximum robot speed.
Note
For speed restriction expressed in a percent, speed_limit will be used exactly as a percent belonging to [0..100] range, not [0.0..1.0] range.
Create a new image with a PGM/PNG/BMP format: copy depot.pgm main map which will be used in a world simulation from a Nav2 repository to a new depot_speed.pgm file. Open depot_speed.pgm in your favourite raster graphics editor and fill speed restricted areas with grey colors. In our example darker colors will indicate areas with higher speed restriction:
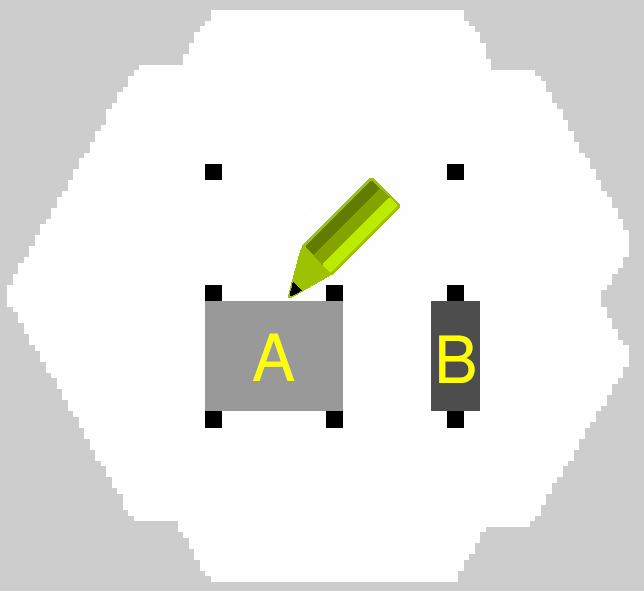
Area “A” is filled with 25% gray color, area “B” - with 50% gray, that means that speed restriction will take 100% - 25% = 75% in area “A” and 100% - 50% = 50% in area “B” from maximum speed value allowed for this robot.
We will use scale map mode with no thresholds. In this mode darker colors will have higher OccupancyGrid values. E.g. for area “B” with 50% of gray OccupancyGrid data will be equal to 50. So in order to hit the target, we need to choose base = 100.0 and multiplier = -1.0. This will reverse the scale OccupancyGrid values to a desired one. No thresholds (free_thresh occupied_thresh) were chosen for the convenience in the yaml file: to have 1:1 full range conversion of lightness value from filter mask -> to speed restriction percent.
Note
It is typical but not a mandatory selection of base and multiplier. For example, you can choose map mode to be raw. In this case color lightness is being directly converted into OccupancyGrid values. For masks saved in a raw mode, base and multiplier will be equal to 0.0 and 1.0 accordingly.
Another important thing is that it is not necessary to use the whole [0..100] percent scale. base and multiplier coefficients could be chosen so that the speed restriction values would belong to somewhere in the middle of percent range. E.g. base = 40.0, multiplier = 0.1 will give speed restrictions from [40.0%..50.0%] range with a step of 0.1%. This might be useful for fine tuning.
After all speed restriction areas will be filled, save the depot_speed.pgm image.
Like all other maps, the filter mask should have its own YAML metadata file. Copy depot.yaml to speed_mask.yaml. Open speed_mask.yaml and update the fields as shown below (as mentioned before for the scale mode to use whole color lightness range there should be no thresholds: free_thresh = 0.0 and occupied_thresh = 1.0):
image: depot.pgm
->
image: depot_speed.pgm
mode: trinary
->
mode: scale
occupied_thresh: 0.65
free_thresh: 0.25
->
occupied_thresh: 1.0
free_thresh: 0.0
Since Costmap2D does not support orientation, the last third “yaw” component of the origin vector should be equal to zero (for example: origin: [1.25, -5.18, 0.0]). Save speed_mask.yaml and the new filter mask is ready to use.
Note
World map itself and filter mask could have different sizes, origin and resolution which might be useful (e.g. for cases when filter mask is covering smaller areas on maps or when one filter mask is used repeatedly many times, like annotating a speed restricted area for same shape rooms in the hotel). For this case, you need to correct resolution and origin fields in YAML as well so that the filter mask is correctly laid on top of the original map. This example shows using the main map as a base, but that is not required.
2. Configure Costmap Filter Info Publisher Server
Each costmap filter reads incoming meta-information (such as filter type or data conversion coefficients) in messages of nav2_msgs/CostmapFilterInfo type. These messages are being published by Costmap Filter Info Publisher Server. The server is running as a lifecycle node. According to the design document, nav2_msgs/CostmapFilterInfo messages are going in a pair with OccupancyGrid filter mask topic. Therefore, along with Costmap Filter Info Publisher Server there should be enabled a new instance of Map Server configured to publish filter masks.
In order to enable Speed Filter in your configuration, both servers should be enabled as lifecycle nodes in Python launch-file. For example, this might look as follows, though adding them as Composition Nodes to your Navigation Component Container is also possible:
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument, GroupAction, SetEnvironmentVariable
from launch.conditions import IfCondition
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration, PythonExpression
from launch_ros.actions import LoadComposableNodes, Node, PushROSNamespace, SetParameter
from launch_ros.descriptions import ComposableNode, ParameterFile
from nav2_common.launch import LaunchConfigAsBool, RewrittenYaml
def generate_launch_description() -> LaunchDescription:
# Get the launch directory
bringup_dir = get_package_share_directory('nav2_bringup')
namespace = LaunchConfiguration('namespace')
speed_mask_yaml_file = LaunchConfiguration('speed_mask')
use_sim_time = LaunchConfigAsBool('use_sim_time')
autostart = LaunchConfigAsBool('autostart')
params_file = LaunchConfiguration('params_file')
use_composition = LaunchConfigAsBool('use_composition')
container_name = LaunchConfiguration('container_name')
container_name_full = (namespace, '/', container_name)
use_respawn = LaunchConfigAsBool('use_respawn')
use_speed_zones = LaunchConfigAsBool('use_speed_zones')
log_level = LaunchConfiguration('log_level')
lifecycle_nodes = ['speed_filter_mask_server', 'speed_costmap_filter_info_server']
# Map fully qualified names to relative ones so the node's namespace can be prepended.
remappings = [('/tf', 'tf'), ('/tf_static', 'tf_static')]
yaml_substitutions = {
'SPEED_ZONE_ENABLED': use_speed_zones,
}
configured_params = ParameterFile(
RewrittenYaml(
source_file=params_file,
root_key=namespace,
param_rewrites={},
value_rewrites=yaml_substitutions,
convert_types=True,
),
allow_substs=True,
)
stdout_linebuf_envvar = SetEnvironmentVariable(
'RCUTILS_LOGGING_BUFFERED_STREAM', '1'
)
declare_namespace_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'namespace', default_value='', description='Top-level namespace'
)
declare_speed_mask_yaml_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'speed_mask',
default_value='',
description='Full path to speed mask yaml file to load',
)
declare_use_sim_time_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'use_sim_time',
default_value='false',
description='Use simulation (Gazebo) clock if true',
)
declare_params_file_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'params_file',
default_value=os.path.join(bringup_dir, 'params', 'nav2_params.yaml'),
description='Full path to the ROS2 parameters file to use for all launched nodes',
)
declare_use_composition_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'use_composition',
default_value='False',
description='Use composed bringup if True',
)
declare_container_name_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'container_name',
default_value='nav2_container',
description='the name of container that nodes will load in if use composition',
)
declare_use_respawn_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'use_respawn',
default_value='False',
description='Whether to respawn if a node crashes. Applied when composition is disabled.',
)
declare_use_speed_zones_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'use_speed_zones', default_value='True',
description='Whether to enable speed zones or not'
)
declare_log_level_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'log_level', default_value='info', description='log level'
)
load_nodes = GroupAction(
condition=IfCondition(PythonExpression(['not ', use_composition])),
actions=[
PushROSNamespace(namespace),
SetParameter('use_sim_time', use_sim_time),
Node(
condition=IfCondition(use_speed_zones),
package='nav2_map_server',
executable='map_server',
name='speed_filter_mask_server',
output='screen',
respawn=use_respawn,
respawn_delay=2.0,
parameters=[configured_params, {'yaml_filename': speed_mask_yaml_file}],
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', log_level],
remappings=remappings,
),
Node(
condition=IfCondition(use_speed_zones),
package='nav2_map_server',
executable='costmap_filter_info_server',
name='speed_costmap_filter_info_server',
output='screen',
respawn=use_respawn,
respawn_delay=2.0,
parameters=[configured_params],
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', log_level],
remappings=remappings,
),
Node(
package='nav2_lifecycle_manager',
executable='lifecycle_manager',
name='lifecycle_manager_speed_zone',
output='screen',
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', log_level],
parameters=[{'autostart': autostart}, {'node_names': lifecycle_nodes}],
),
],
)
# LoadComposableNode for map server twice depending if we should use the
# value of map from a CLI or launch default or user defined value in the
# yaml configuration file. They are separated since the conditions
# currently only work on the LoadComposableNodes commands and not on the
# ComposableNode node function itself
load_composable_nodes = GroupAction(
condition=IfCondition(use_composition),
actions=[
PushROSNamespace(namespace),
SetParameter('use_sim_time', use_sim_time),
LoadComposableNodes(
target_container=container_name_full,
condition=IfCondition(use_speed_zones),
composable_node_descriptions=[
ComposableNode(
package='nav2_map_server',
plugin='nav2_map_server::MapServer',
name='speed_filter_mask_server',
parameters=[
configured_params,
{'yaml_filename': speed_mask_yaml_file}
],
remappings=remappings,
),
ComposableNode(
package='nav2_map_server',
plugin='nav2_map_server::CostmapFilterInfoServer',
name='speed_costmap_filter_info_server',
parameters=[configured_params],
remappings=remappings,
),
],
),
LoadComposableNodes(
target_container=container_name_full,
composable_node_descriptions=[
ComposableNode(
package='nav2_lifecycle_manager',
plugin='nav2_lifecycle_manager::LifecycleManager',
name='lifecycle_manager_speed_zone',
parameters=[
{'autostart': autostart, 'node_names': lifecycle_nodes}
],
),
],
),
],
)
# Create the launch description and populate
ld = LaunchDescription()
# Set environment variables
ld.add_action(stdout_linebuf_envvar)
# Declare the launch options
ld.add_action(declare_namespace_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_speed_mask_yaml_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_sim_time_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_params_file_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_composition_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_container_name_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_respawn_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_use_speed_zones_cmd)
ld.add_action(declare_log_level_cmd)
# Add the actions to launch all of the map modifier nodes
ld.add_action(load_nodes)
ld.add_action(load_composable_nodes)
return ld
where the params_file variable should be set to a YAML-file having ROS parameters for Costmap Filter Info Publisher Server and Map Server nodes. These parameters and their meaning are listed at Map Server page. Please, refer to it for more information. The example of params_file could be found below:
speed_filter_mask_server:
ros__parameters:
topic_name: "speed_filter_mask"
# yaml_filename: ""
speed_costmap_filter_info_server:
ros__parameters:
type: 1
filter_info_topic: "speed_costmap_filter_info"
mask_topic: "speed_filter_mask"
base: 100.0
multiplier: -1.0
Note, that:
For Speed Filter setting speed restrictions in a percent from maximum speed, the
typeof costmap filter should be set to1. All possible costmap filter types could be found at Map Server page.Filter mask topic name should be the equal for
mask_topicparameter of Costmap Filter Info Publisher Server andtopic_nameparameter of Map Server.As was described in a previous chapter,
baseandmultipliershould be set to100.0and-1.0accordingly for the purposes of this tutorial example.
3. Enable Speed Filter
Costmap Filters are Costmap2D plugins. You can enable the SpeedFilter plugin in Costmap2D by adding speed_filter to the plugins parameter in nav2_params.yaml. The Speed Filter plugin should have the following parameters defined:
plugin: type of plugin. In our casenav2_costmap_2d::SpeedFilter.filter_info_topic: filter info topic name. This needs to be equal tofilter_info_topicparameter of Costmap Filter Info Publisher Server from the chapter above.speed_limit_topic: name of topic to publish speed limit to.
Full list of parameters supported by SpeedFilter are listed at the Speed Filter Parameters page.
You can place the plugin either in the global_costmap section in nav2_params.yaml to have speed restriction mask applied to global costmap or in the local_costmap to apply speed mask to the local costmap. However, SpeedFilter plugin should never be enabled simultaneously for global and local costmaps. Otherwise, it can lead to unwanted multiple “speed restriction” - “no restriction” message chains on speed restriction boundaries, that will cause jerking of the robot or another unpredictable behaviour.
In this tutorial, we will enable Speed Filter for the global costmap. For this use the following configuration:
global_costmap:
global_costmap:
ros__parameters:
...
plugins: ["static_layer", "obstacle_layer", "inflation_layer"]
filters: ["speed_filter"]
...
speed_filter:
plugin: "nav2_costmap_2d::SpeedFilter"
enabled: True
filter_info_topic: "speed_costmap_filter_info"
speed_limit_topic: "speed_limit"
As stated in the design, Speed Filter publishes speed restricting messages targeted for a Controller Server so that it could restrict maximum speed of the robot when it needed. Controller Server has a speed_limit_topic ROS parameter for that, which should be set to the same as in speed_filter plugin value. This topic in the map server could also be used to any number of other speed-restricted applications beyond the speed limiting zones, such as dynamically adjusting maximum speed by payload mass.
Set speed_limit_topic parameter of a Controller Server to the same value as it set for speed_filter plugin:
controller_server:
ros__parameters:
...
speed_limit_topic: "speed_limit"
4. Run Nav2 stack
Ready-to-go standalone Python launch-script, YAML-file with ROS parameters and filter mask example for Speed Filter could be found in nav2_bringup directory. To run the demo, simply launch as follows:
ros2 launch nav2_bringup tb4_simulation_launch.py
For better visualization of speed filter mask, in RViz in the left Displays pane unfold Map and change Topic from /map -> to /speed_filter_mask.
Set the goal behind the speed restriction areas and check that the filter is working properly: robot should slow down when going through a speed restricting areas. Below is how it might look:
Note
For another example and additional context, check the Navigation2 tutorials https://github.com/ros-navigation/navigation2_tutorials/tree/rolling/nav2_costmap_filters_demo