Iron to Jazzy
Moving from ROS 2 Iron to Jazzy, a number of stability improvements were added that we will not specifically address here.
BehaviorTree.CPP upgraded to version 4.5+
Since we migrated from version 3.8 to 4.5, users must upgrade their XML and source code accordingly.
You can refer to [this page](https://www.behaviortree.dev/docs/migration) for more details, but the main changes are:
XML must be changed. This [python script can help](https://github.com/BehaviorTree/BehaviorTree.CPP/blob/master/convert_v3_to_v4.py).
The syntax of SubTrees has changed; the one of SubTreePlus was adopted, instead.
If you created a custom ControlNode or DecoratorNode, you must handle the case when a child returns BT::NodeStatus::SKIPPED.
Added TwistStamped Option for Commands
A new parameter enable_stamped_cmd_vel has been added to all of the publishers and subscribers of cmd_vel and related topics. This allows you to set the publication and subscription of TwistStamped messages over Twist messages to have frame and timestamp information of the set command. For now, this is default to false to not change current behavior, but it is planned to make TwistStamped the default behavior alongside Gazebo, ROS 2 Control, and related projects.
Add VelocityPolygon in Collision Monitor
PR #3708 adds VelocityPolygon type in Collision Monitor. This allows the user to setup multiple polygons to cover the range of the robot’s velocity limits. For example, the user can configure different polygons for rotation, moving forward, or moving backward. The Collision Monitor will check the robot’s velocity against each sub polygon to determine the appropriate polygon to be used for collision checking. The tutorial is available in the Configuring Collision Monitor with VelocityPolygon section.
Change polygon points parameter format in Collision Monitor
PR #4020 changes the format of the Polygon points parameter from vector<double> to string. This makes the polygon description more uniform across the Collision Monitor and Costmap_2D.
Now we can define a polygon’s points in string that has a vector<vector<double>> structure like this "[[p1.x, p1.y], [p2.x, p2.y], [p3.x, p3.y],...]" with a minimum of 4 points described. An example of a Square polygon will be written as follows.
PolygonFront:
type: "polygon"
points: "[[0.3, 0.3], [0.3, -0.3], [0.0, -0.3], [0.0, 0.3]]"
action_type: "none"
min_points: 4
visualize: True
polygon_pub_topic: "polygon_front"
Introduction of Soft-Real Time Action Servers
PR #3914 adds soft real-time prioritization to the controller server to better ensure resources to time sensitive portions of the codebase. The Simple Action Server now has a realtime input field exposed in the Controller Server via the parameter use_realtime_priority which will set the controller’s execution thread to a higher priority than the rest of the system to meet scheduling deadlines. To use this feature, you use set the following inside of /etc/security/limits.conf to give userspace access to elevated prioritization permissions. This is currently only enabled in the Controller Server, who’s execution thread is sensitive to scheduling priorities, but could be set with other threads in the future if found necessary.
<username> soft rtprio 99
<username> hard rtprio 99
The Collision Monitor and Velocity Smoothers also had use_realtime_priority added as well!
Introduce a new Multi-Robot Bringup Launch
PR #3572 introduces a new way of bringup tb3 multi-robot that names as cloned_tb3_simulation_launch.py for simulation. cloned_tb3_simulation_launch.py enables to bring up multiple robots with same parameter that described in nav2_multirobot_param_all.yaml. And multiple robots are separated by namespaces which are given as a Launch Arguments.
Existing multi_tb3_simulation_launch.py which was utilized in previous is replaced with unique_tb3_simulation_launch.py, allowing for multiple unique robot instances utilizing nav2_multirobot_params_<N>.yaml configuration files.
New option for the Voxel and Obstacle Layers
PR #3612 adds a new MaxWithoutUnknownOverwrite option to combination_method parameter in Voxel and Obstacle Layers. This can be used to make sure that the static map is the dominant source of information, and easily prevent the robot to go through places that are not present in the static map.
use_interpolation RPP Parameter Depreciated
After a distribution of testing by many users, we have depreciated the use_interpolation parameter and it is now default on at all times without the ability to disable. It improves velocity smoothness and overall quality of tracking positively in all cases.
Changes to MPPI Goal Critic
The MPPI Goal critic’s formulation is changed to better keep up with speed on approach to goal instead of preemptively slowing too significantly. It also allows you to better use the weight to adjust the degree at which it slows more naturally. This change involves adjusting the threshold_to_consider to be the same as your prediction horizon (e.g. samples * dt * max speed) for both the goal critic and path follower critic to have a good hand-off between them without deceleration.
Changes to MPPI Path Angle Critic
MPPI’s Path Angle critic now has a mode setting to adjust behavior depending on robot’s desired behavioral traits. Previously, it penalized path orientations that deviated far the the robot’s forward orientation to turn the robot towards sharp changes in the path. This is still default (mode: 0), but other modes now exist too.
mode: 1 sets the penalization of path’s relative directions by either forward orientation or the opposite for reversing to allow for true bidirectional motion when one way or another is not preferable for a symmetric robot. This uses only the path’s relative points to the robot to decide which direction to incentivize.
mode: 2 instead uses the path’s orientations when a feasible path is given from the Smac Planners or the Smoother server’s algorithms. This way, the globally planned orientations are followed rather than the based solely on the path’s relative points. This is useful for non-circular robots in highly confined settings where there may be restricted opportunities to change directions so following the global path’s orientation are required to end in the orientation you require.
Changes to MPPI Path Handling For Directionality
MPPI’s Path Align Critic and Path Handler object now have options to utilize the path’s orientation information to force the controller to change directions when and only when requested by a feasible planner. When enforce_path_inversion is true, the path handler will prune the path to the first time the directions change to force the controller to plan to the inversion point and then be set the rest of the path, once in tolerance. The Path Align critic also contains a parameter use_path_orientations which can be paired with it to incentivize aligning the path containing orientation information to better attempt to achieve path inversions where requested and not do them when not requested.
See MPPI’s configuration guide for complete information.
Addition of new MPPI Cost Critic
Analog to the ObstacleCritic, the CostCritic is another obstacle avoiding critic alternative if the ObstacleCritic is not working well for you.
This critic uses the inflated costs in the costmap to score rather than distance to obstacles as the ObstaclesCritic does.
See the configuration guide for more information.
MPPI Acceleration
New to Jazzy, MPPI is 45% faster due to a weeks long optimization campaign. Enjoy!
Move Error Code Enumerations
PR #3693 moves the enumeration codes from the goal to the result section.
Substitution in parameter file
Enabled substitution in parameter file. For example, you can write the following
bt_navigator:
ros__parameters:
default_nav_to_pose_bt_xml: $(find-pkg-share my_package)/behavior_tree/my_nav_to_pose_bt.xml
For more information about substitutions syntax, see here
Allow Behavior Server Plugins to Access The Action Result
PR #3704 allows behavior servers plugins to access and modify the action result.
Smac Planner Debug Param Name Change
debug_visualizations replaces viz_expansions parameter in Hybrid-A* to reflect the new inclusion of footprint debug information being published as well.
Smac Planner On Approach to Goal Shortcutting Solutions
PR #3962 adds new params analytic_expansion_max_cost and analytic_expansion_max_cost_override in extension of analytic_expansion_max_length in Humble to further limit potential shortcutting of paths near obstacles in close proximity to the goal.
It uses a maximum cost parameter (default 200) to tell if an expansion is closer to an obstacle than a user would like. If the expansion is critically close to the goal, then it may override this constraint if analytic_expansion_max_cost_override is false - allowing the constraint to be overridden to find a successful path solution, as it may be required.
This PR also introduces additional analytic expansion scoring logic and edge case handling to improve path qualities by an analog heuristic function.
Added GPS Waypoint Follower Server
This PR 2814 adds the follow_gps_waypoints action server in nav2_waypoint_follower. This server accepts a set of GPS goals instead of cartesian goals and provides all the other functionalities available on nav2_waypoint_follower. A new tutorial demonstrating its functionality was also added on PR 70 on navigation2_tutorials and can be found on the General Tutorials directory on this website.
Smac Planner Hybrid-A* New Features
New features allow_primitive_interpolation which allows for more primitives in the search set, use_quadratic_cost_penalty to impact the cost penalty order in the traversal and heuristic functions, and downsample_obstacle_heuristic to optionally not downsample the obstacle heuristic’s costmap were added. The default behavior will remain the same. If you would like to use these new features, please check out the Smac Planner Hybrid-A* configuration guide.
Dynamic enabling/disabling of sources/polygons in Collision Monitor/Detector
In this PR #3825 we added the ability to dynamically enable/disable sources and polygons in the Collision Monitor/Detector.
Expose action server’s result timeout
In this PR #3787 the timeout for action server’s result was exposed in all nodes having action servers.
This is because in this PR #1012 in rcl a change was introduced which makes action servers discard a goal handle if the result
is not produced within 10 seconds, when the default was set to 15 minutes before. Since some actions in Nav2 may take more than 10 seconds to complete, the user has now the ability
to set this value through the action_server_result_timeout parameter, which defaults to 15 minutes in the bt_navigators and waypoint_follower and to 10 seconds in all other nodes.
RewrittenYaml could add new parameters to YAMLs
Now RewrittenYaml widely used in Nav2 launch-scripts, could do not only substitutions of ROS-parameters existing in original YAML, but rather additions of new parameters, that did not exist in the YAML. Certainly, these parameters should be declared for target ROS-nodes, otherwise they won’t be processed in run-time. In such functionality, they should be expressed in absolute values, separated by a dot. For example, the rewrite for a prune_distance parameter of a FollowPath node will look like 'controller_server.ros__parameters.FollowPath.prune_distance': '1.0' in a param_rewrites dictionary of RewrittenYaml() argument.
The change was intoroduced in the scope of PR #3785 fix.
Simple Commander API Allows Multi-Robot Namespacing
The Simple Navigator API now allows multi-robot namespacing by exposing a namespace field in the constructor to allow you to specify the Nav2 stacks’ namespace for a robot or system. See this PR for details.
Change duration type in wait_action node
In this PR #3871 the type of duration variable in wait_action node is changed from int to double, which allows you to use floating values for wait_action.
The costmap activation fails when required transforms are not available
In this PR #3866 the parameter initial_transform_timeout is added to the costmap. The activation of the costmap now fails,
if the transformation from the robot base frame to the global frame does not become available during this timeout.
Collision Monitor: added watchdog mechanism based on source_timeout parameter with default blocking behavior
PR #3880 adds a watchdog mechanism that stops the robot if a source data is not published yet, or if no new data is received within the source_timeout` parameter, or if impossible to transform data to base frame. source_timeout parameter can now be set per source: if source_timeout is not set for a source, the value of the node source_timeout parameter is used.
Additionally, this watchdog mechanism can be disabled by setting source_timeout: 0.0.
BtActionServer: use native library haltTree()
PR #3950 changes the method used by BehaviorTreeEngine::haltAllActions to halt the BT nodes to the bt.cpp native method haltTree().
Before this change, only the active BT node was halted when finishing the action. After this change, all BT nodes halt() methods are called. This is very convenient to handle cleaning operation (switch off your lights when leaving) in halt().
Also updated nav2_behavior_tree::BtActionServer::haltTree() to use the same. It is used nowhere in nav2 but is useful for external users (like me) that want for instance to halt the tree on preemption.
Global Frame Removed from 2 BT Nodes
The Global Frame was removed from RemovePassedGoals and GoalReached BT nodes and instead using the frame_id of the goal’s headers for transformation.
Introduction of CostmapUpdate.msg
PR #3965 introduces a new type of message - CostmapUpdate.msg. It is the update message related to the Costmap.msg. Now instead of sending the whole costmap in every message, such as with Costmap.msg, the CostmapUpdate.msg includes only the area of the costmap that has changed since the previous update message. The Costmap.msg is sent only once at the beginning, followed by the messages of the CostmapUpdate.msg type. The idea is to mimic the OccupancyGrid.msg and OccupancyGridUpdate.msg behavior.
To activate this feature, the Costmap2D ROS parameter always_send_full_costmap has to be set to false.
To subscribe to Costmap.msg and CostmapUpdate.msg it is recommended to use the CostmapSubscriber class.
Full Stack Uses Node Clocks
The stack no longer contains wall timers or wall rates. It will now use the node clocks. This will be ROS Time for simulation when use_sim_time is true. Else, it uses a steady clock.
New Graceful Motion Controller
PR #4021 introduces a new type of controller for differential robots based on a pose-following kinematic control law that generates a smooth and comfortable trajectory.
See Graceful Controller for more information.
New RViz Plugin for selecting Planners, Controllers, Goal Checkers, Progress Checkers and Smoothers
In PR #4091 a new RViz plugin was added to select the planner, controller, goal checker, progress checker, and smoother on the fly.
The primary goal of this plugin is to facilitate the developers and easy integration testing of their configuration before deploying the robot in the intended application.
In order to facilitate the dynamic selection of the specified components, the BT selector nodes for all these components were utilized and were updated to all the relevant BT nodes.
Here we can see the working demo of the plugin:
In the GIF, it can be seen that there are two controller_ids namely, FollowPath and HighSpeedFollowPath. By default, the one defined in the Behavior tree is utilized.
In this case, the FollowPath is the default controller_id. The difference between the two controller_ids is that HighSpeedFollowPath has a higher max velocity compared to the FollowPath. This difference can be well noted in the GIF.
Attention
If a server is unavailable, then the combo box or the drop down list of the particular component will be empty.
RPP new optional interpolate_curvature_after_goal behavior and fix conflict between use_rotate_to_heading and allow_reversing
In PR #4140 a new optional interpolate_curvature_after_goal parameter (default false) was added that activates the interpolation of a carrot after the goal in order to maintain a constant curvature lookahead distance. This is to avoid instabilities at the end of the path on the generation of the angular speed. The carrot used for the linear speed computation stays the same.
Interpolation is based on the orientation of the vector formed by the last 2 poses of the path. Hence paths of length 1 are rejected when interpolate_curvature_after_goal is true. It can be used only when use_fixed_curvature_lookahead: true.

Additionally, the conflict between use_rotate_to_heading and allow_reversing was fixed so use_rotate_to_heading can now be used backward.
Cancel Checker Interface For GlobalPlanner
PR #4148 introduces a new interface for the GlobalPlanner to allow for the cancellation of the current planning task.
Before the planners would continue to plan even if the goal was cancelled, now they can check it and stop planning if the goal is cancelled.
New interface for GlobalPlanner::createPlan:
virtual nav_msgs::msg::Path createPlan(
const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & start,
const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & goal,
std::function<bool()> cancel_checker)
This is implemented for all the planners in the stack, you can check them for the example use of cancel_checker function (simply check cancel_checker()).
Smac and Theta* planners have a new parameter terminal_checking_interval which is the frequency of the cancel or timeout checking in terms of number of iterations.
New collision monitor parameter
PR #4207 introduces a new boolean parameter polygon_subscribe_transient_local (value is false by default), which set the QoS durability for polygon topic or footprint topic subscription.
New graceful cancellation API for Controllers
PR #4136 introduces a new graceful cancellation API for controllers. Previously when a goal was canceled, the controller would stop the robot immediately. This API allows the controller to stop the robot in a more graceful way. The new API is implemented in the RegulatedPurePursuitController by adding a new parameter cancel_deceleration. So when the goal is canceled, a constant deceleration will be used while continuing to track the path to stop the robot instead of stopping immediately. This API can be should be added to all controllers that have acceleration limits.
Standardization of Plugin Naming with Double Colons (::)
PR #4220 standardizes plugin naming across the Navigation2 package to use double colons (::), replacing the previous mixed use of slashes (/) and double colons. Affected plugins include:
Behavior Server:
nav2_behaviors::Spin,nav2_behaviors::BackUp,nav2_behaviors::DriveOnHeading,nav2_behaviors::Wait,nav2_behaviors::AssistedTeleopPlanner Server:
nav2_navfn_planner::NavfnPlanner,nav2_smac_planner::SmacPlanner2D,nav2_smac_planner::SmacPlannerHybrid,nav2_theta_star_planner::ThetaStarPlannerController Server:
nav2_regulated_pure_pursuit_controller::RegulatedPurePursuitController,nav2_dwb_controller::DWBLocalPlannerBT Navigator:
nav2_bt_navigator::NavigateToPoseNavigator,nav2_bt_navigator::NavigateThroughPosesNavigator
Collision monitor: dynamic radius for circle type polygons
PR #4226 introduces usage of parameter <polygon_name>.polygon_sub_topic for circle type polygons. If parameter <polygon_name>.radius is not set, collision monitor node subscribes to topic <polygon_name>.polygon_sub_topic (subscription type is std_msgs/msg/Float32), and the current circle polygon radius will be updating accordingly to received messages on topic.
Static Layer: new parameter footprint_clearing_enabled
PR #4282 introduces usage of parameter footprint_clearing_enabled for the static layer. It works similarly to the footprint_clearing_enabled parameter in the obstacle and voxel layer. If set to true, the static layer will clear the costmap cells that are within the robot’s footprint. It is false by default to keep the previous behavior.
Lifecycle Node: added bond_heartbeat_period parameter (and allow disabling the bond mechanism)
PR #4342 adds the parameter bond_heartbeat_period to the lifecycle nodes to customize the bond mechanism publishing period (on the /bond topic). Default value is 0.1s. Disabled if inferior or equal to 0.0.
Rotation Shim Controller: new parameter rotate_to_goal_heading
PR #4332 introduces usage of parameter rotate_to_goal_heading for the rotation shim controller. It allows the rotation shim controller to take back control when reaching the XY goal tolerance to perform a clean rotation towards the goal heading. Some controllers will do this internally, but it is a useful option for others.
MPPI Controller: Addition of acceleration constraints
PR #4352 adds new parameters ax_max, ax_min, ay_max, az_max for the MPPI controller. These parameters will enable the MPPI controller to generate local trajectories within the specified acceleration constraints.
RegulatedPurePursuit Controller [RPP]: new parameter use_cancel_deceleration
PR #4441 adds a new parameter use_cancel_deceleration for the regulated pure pursuit controllers. This parameter enables the controller to use a constant deceleration to stop the robot gracefully instead of stopping immediately when a goal is canceled.
Clear Costamp Around Passed Pose
In PR #5309, a new service was added to the nav2_costmap_2d package to clear the costmap around a passed pose.
A service client was also added to the clear costmap plugin in the nav2_behavior_tree package.
This is particularly useful in scenarios where the planner fails due to outdated costmap data at the goal location which is outside of your obstacle/raytrace range—often caused by dynamic obstacles that have since moved. Instead of clearing the entire costmap as a recovery behavior, this feature would enable targeted clearing, preserving useful map data.
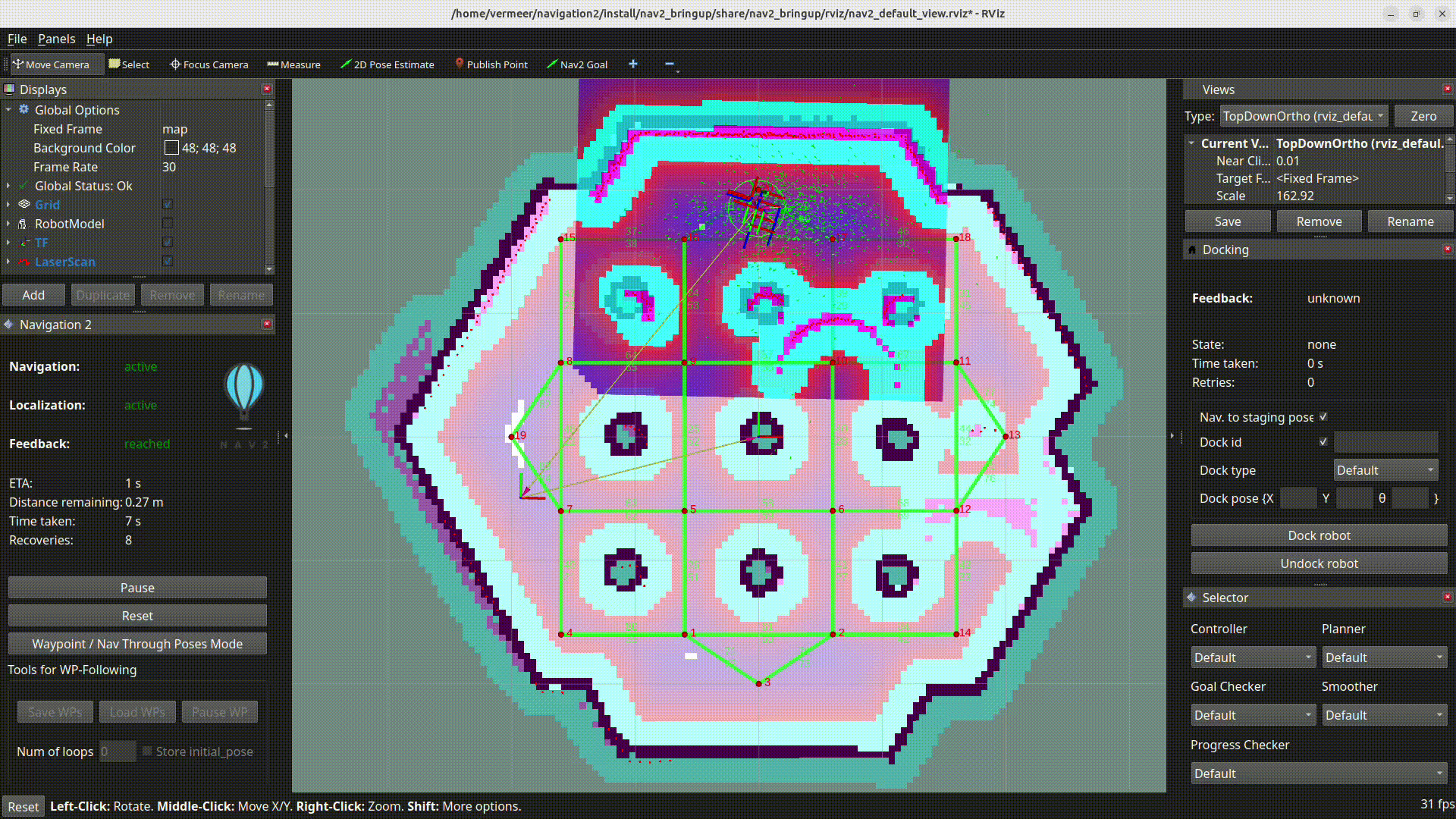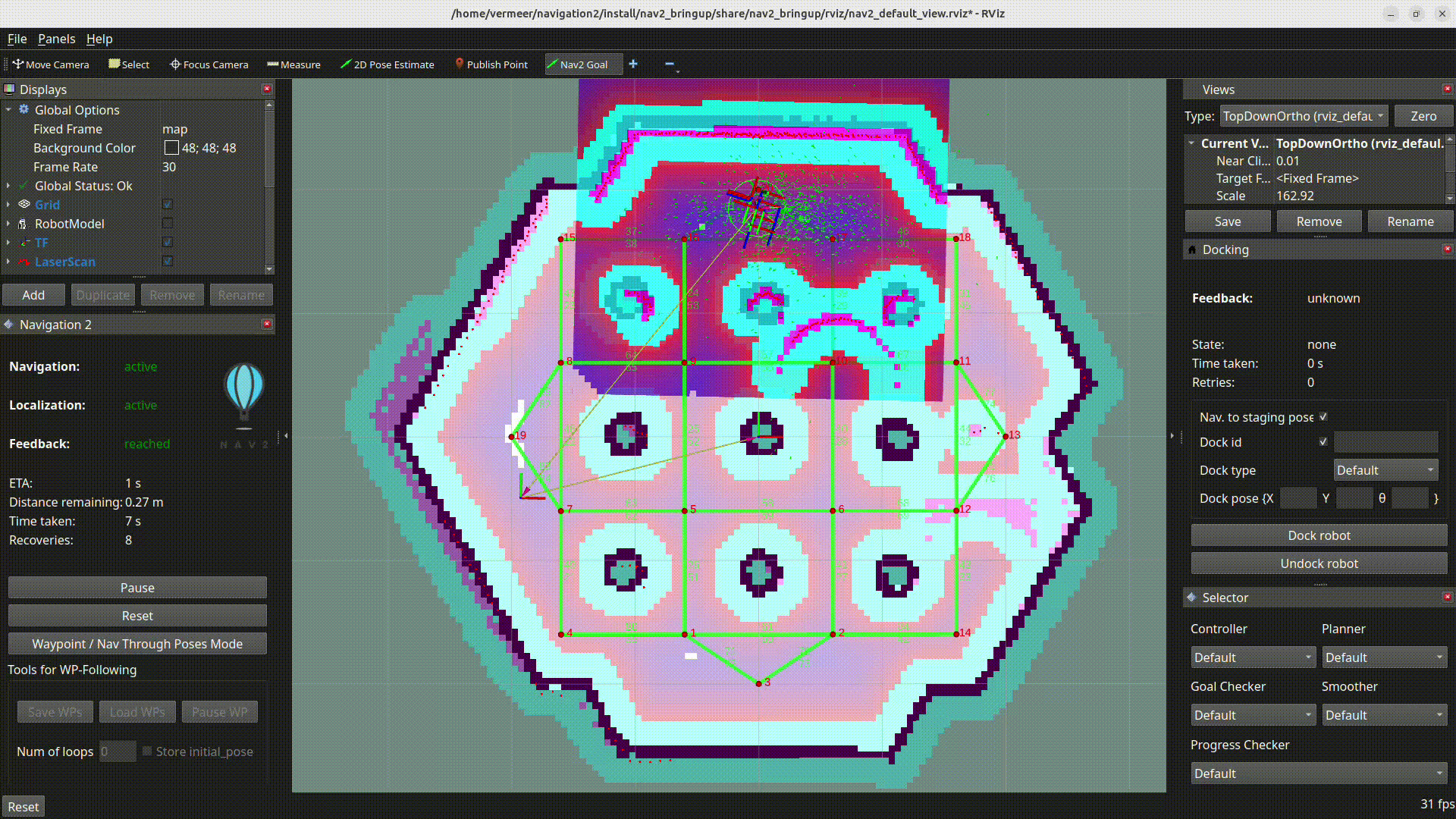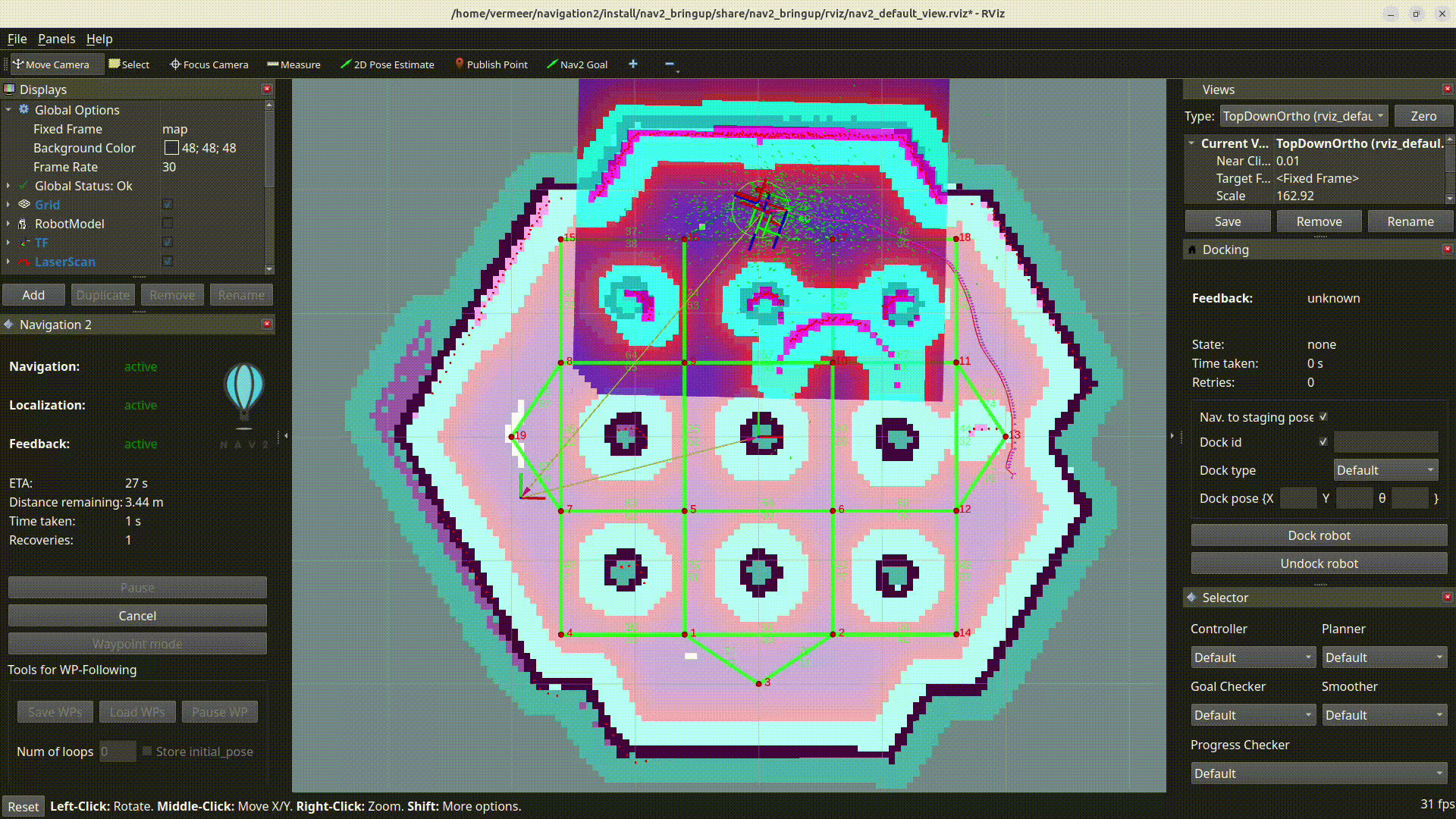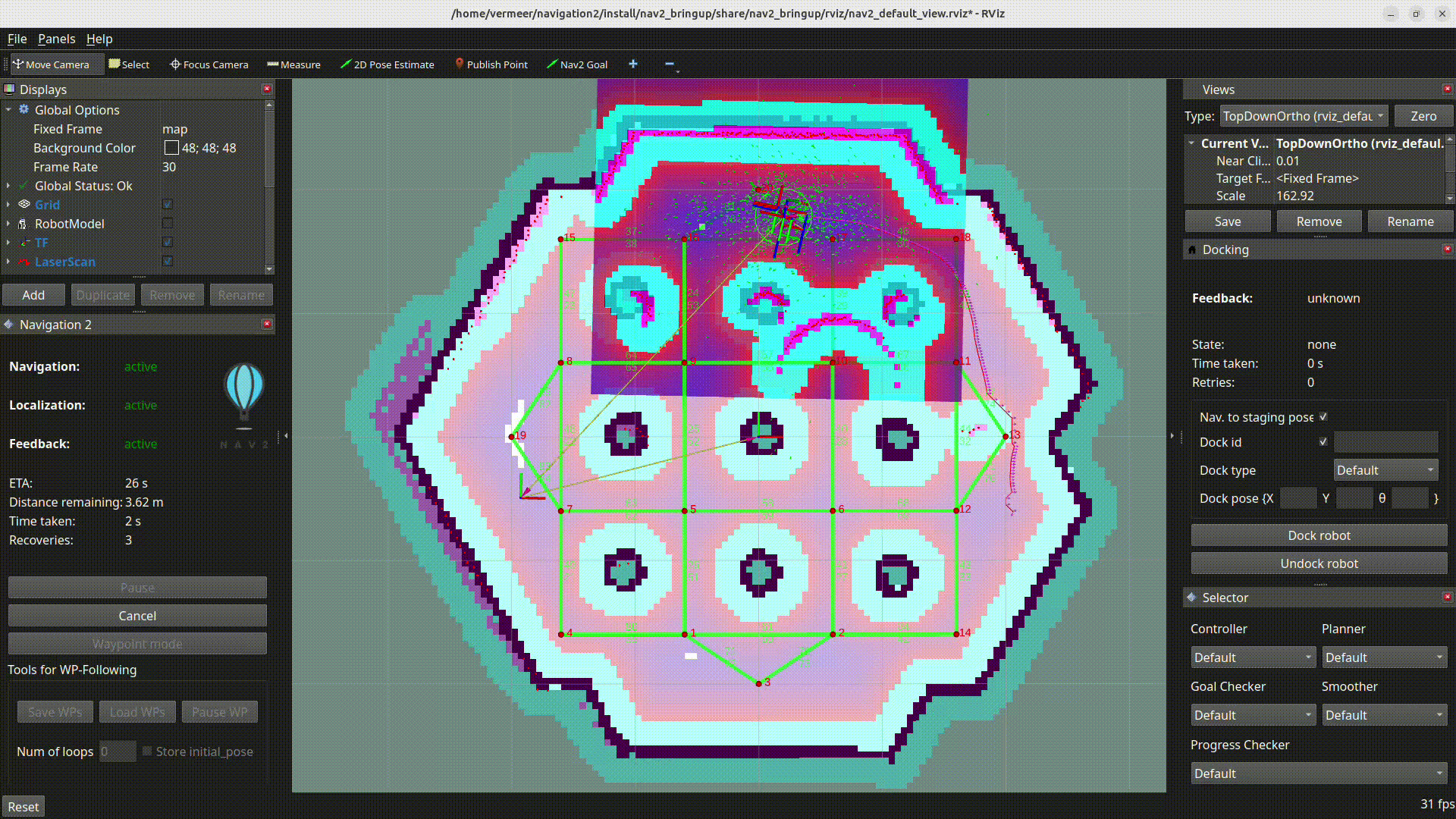
RViz visualization shows an example of clearing outdated cost at the desired goal location, this would have previously caused planners like SMAC planner to fail.
The following is an example of how to use ClearCostmapAroundPose in a behavior tree to clear the costmap around a goal pose in the event that the planner fails to compute a path.
<RateController hz="1.0">
<RecoveryNode number_of_retries="1" name="ComputePathToPose">
<ComputePathToPose goal="{goal}" path="{path}" planner_id="{selected_planner}" error_code_id="{compute_path_error_code}" error_msg="{compute_path_error_msg}"/>
<ClearCostmapAroundPose name="ClearCostmapAroundPose-Context" service_name="global_costmap/clear_around_pose_global_costmap" pose="{goal}" reset_distance="5.0"/>
</RecoveryNode>
</RateController>